Ear irrigation is a common procedure to remove excess cerumen using a bulb syringe. It ensures proper hearing and prevents infections. Proper technique is crucial for safety and effectiveness. Incorrect methods can cause ear trauma or infections. Always performed by trained healthcare professionals for optimal results.

1.1 Definition and Purpose of Ear Irrigation
Ear irrigation is a non-invasive medical procedure designed to remove excess cerumen (earwax) and debris from the external auditory canal. The primary purpose of this technique is to restore hearing clarity‚ alleviate discomfort‚ and prevent potential infections caused by blockages. It involves the controlled use of a bulb syringe or similar device to gently flush the ear canal with warm water‚ ensuring the removal of obstructions while preserving ear health. This procedure is essential for individuals experiencing cerumen impaction‚ which can lead to hearing loss‚ itching‚ or a sensation of fullness in the ear. Properly executed ear irrigation promotes auditory function and maintains ear hygiene‚ making it a vital component of otologic care.
1.2 Importance of Proper Ear Irrigation Techniques
Proper ear irrigation techniques are crucial to ensure the procedure’s safety and effectiveness. Improper methods can lead to ear trauma‚ infections‚ or incomplete wax removal‚ potentially causing hearing loss or discomfort. Using correct methods prevents damage to the delicate structures of the ear‚ such as the eardrum and ossicles. Proper techniques involve using a bulb syringe with warm water‚ avoiding deep insertion‚ and maintaining gentle pressure. This minimizes the risk of complications and ensures the ear canal remains intact. Effective irrigation restores hearing clarity‚ alleviates symptoms like itching‚ and prevents infections. Trained healthcare professionals should always perform the procedure to guarantee adherence to best practices and patient safety. Proper techniques are essential for achieving successful outcomes and maintaining ear health.

Pre-Irrigation Guidelines and Preparation
Pre-irrigation involves patient assessment‚ ensuring eligibility‚ and gathering necessary materials like a bulb syringe and ear drops. Patient education on risks and benefits is essential for informed consent.
2.1 Patient Assessment and Eligibility Criteria
Patient assessment is critical before ear irrigation to ensure eligibility. A healthcare provider evaluates for contraindications‚ such as a perforated eardrum or active infection. The patient’s history‚ symptoms‚ and physical examination findings guide eligibility. Conditions like ear pain or discharge may require further evaluation. The procedure is typically avoided in individuals with a history of ear surgery or trauma. Eligibility criteria are based on clinical guidelines to minimize risks. Patient-specific factors‚ such as age‚ mobility‚ and ability to follow instructions‚ are also considered. Proper assessment ensures safe and effective irrigation‚ avoiding complications. Informed consent is obtained after discussing risks and benefits‚ ensuring the patient understands the procedure.
2;2 Necessary Materials and Equipment
The necessary materials for ear irrigation include a bulb syringe‚ ear drops (e.g.‚ olive oil or hydrogen peroxide)‚ gloves‚ and a clean towel or drape. An otoscope is used for pre- and post-procedure examination. A basin or container is needed to catch water and debris. Protective eyewear may be worn by the patient. The syringe should be filled with warm water at body temperature. Additional supplies like cotton balls or gauze can help dry the ear post-procedure. All equipment must be sterile or clean to prevent infection. Ensure the environment is prepared to minimize mess and ensure patient comfort. Proper equipment preparation is essential for a safe and effective irrigation process.
2.3 Patient Education and Informed Consent
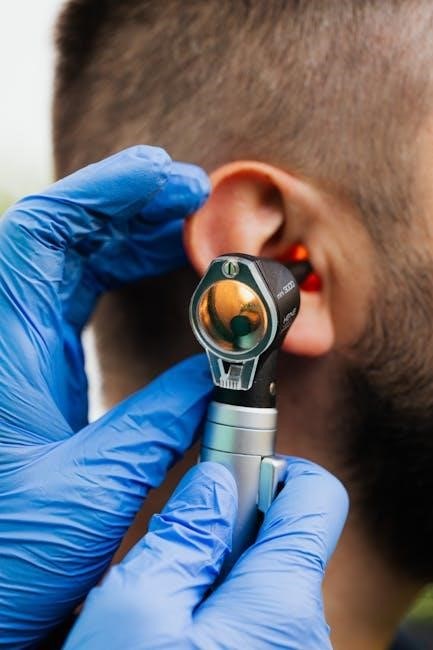
Patient education and informed consent are critical before proceeding with ear irrigation. The healthcare provider must explain the procedure‚ its benefits‚ and potential risks‚ such as ear trauma or discomfort. The patient should be informed about the sensations they may experience during irrigation. It’s essential to discuss any allergies‚ medical history‚ or previous complications. Written consent is typically required‚ ensuring the patient understands and agrees to the procedure. The patient should also be advised on post-care instructions and when to seek further medical attention. Clear communication helps build trust and ensures the patient is prepared‚ reducing anxiety and promoting cooperation during the process.
Step-by-Step Ear Irrigation Procedure
Ear irrigation involves using a bulb syringe to gently flush out cerumen. The process includes examining the ear‚ identifying wax‚ and irrigating with proper technique to ensure safety and effectiveness.
3.1 Ear Examination and Wax Identification
Ear examination is the first step in the irrigation process. It involves using an otoscope to visualize the ear canal and identify cerumen buildup. The healthcare provider assesses the location‚ consistency‚ and amount of wax to determine if irrigation is suitable. Signs of excessive cerumen include hearing loss‚ itching‚ or a plugged sensation. The examination also checks for any contraindications‚ such as a perforated eardrum or acute infection‚ which may require alternative treatments. Proper identification ensures safe and effective irrigation‚ avoiding potential complications. This step is crucial for guiding the procedure and ensuring patient safety.
3.2 Positioning the Patient for Optimal Access
Proper patient positioning is essential for effective ear irrigation. The patient should sit upright or lie on their side‚ ensuring the affected ear faces upwards. For adults‚ tilting the head slightly backward aligns the ear canal for better access. Children may be positioned on their side or held securely to maintain stillness. The healthcare provider should gently pull the outer ear backward and upward for adults or downward for children to straighten the ear canal. This positioning helps prevent complications and ensures the irrigation fluid reaches the cerumen effectively. Proper alignment is crucial for safe and successful removal of earwax.
3.3 Using Ear Drops for Softening Cerumen
Ear drops are commonly used to soften cerumen before irrigation‚ enhancing the procedure’s safety and effectiveness. Drops like olive oil or hydrogen peroxide are typically administered 2-3 days prior to irrigation. They work by loosening the wax‚ making it easier to remove. Proper administration involves tilting the head and gently instilling the recommended number of drops. The patient should remain in position for a few minutes to allow the drops to penetrate the wax. Softening the cerumen reduces the risk of complications during irrigation‚ such as ear trauma or discomfort. This step is crucial for ensuring a smooth and successful ear irrigation process.
3;4 Irrigation Technique with a Bulb Syringe
Ear irrigation with a bulb syringe is a delicate procedure requiring precision. The syringe is filled with sterile or distilled water at body temperature to avoid causing dizziness. The patient’s ear canal is gently straightened by tilting the head sideways for adults or upward for children. The syringe is aimed at the cerumen‚ avoiding direct pressure on the eardrum. Gentle‚ repeated squeezing of the bulb dislodges the wax. The process is stopped immediately if discomfort occurs. The ear is then dried‚ and the canal is inspected for remaining debris. Proper technique minimizes the risk of trauma or infection‚ ensuring effective cerumen removal.
3.5 Post-Irrigation Ear Canal Inspection
After irrigation‚ a thorough inspection of the ear canal is essential. Using an otoscope‚ the healthcare provider examines the canal for residual cerumen or debris. The tympanic membrane is checked for integrity and mobility. Any signs of trauma‚ such as bleeding or perforation‚ are noted. If cerumen remains‚ additional drops or a follow-up appointment may be recommended. The patient’s hearing is assessed for improvements. Proper documentation of findings ensures continuity of care. This step confirms the procedure’s success and guides further management‚ ensuring patient safety and optimal outcomes. Effective inspection minimizes complications and supports the overall effectiveness of the ear irrigation process.

Safety Measures and Contraindications
Ear irrigation requires strict safety measures‚ including proper training and equipment. Contraindications like eardrum perforation or acute infections must be considered to avoid complications. Always assess eligibility.
4.1 Conditions Where Ear Irrigation is Not Advised
Ear irrigation is contraindicated in cases of eardrum perforation‚ acute otitis media‚ or presence of a foreign body. It should not be performed on patients with a history of ear surgery or trauma. Those with severe ear pain‚ discharge‚ or suspected infections should avoid the procedure. Additionally‚ irrigation is not recommended for individuals with hearing aids or tympanostomy tubes. Patients with impacted cerumen that cannot be softened or those with narrow ear canals are also poor candidates. Always assess for these conditions to prevent complications and ensure safe outcomes;
4.2 Preventing Complications During the Procedure
To prevent complications during ear irrigation‚ use warm water at body temperature to avoid causing dizziness or discomfort. Ensure the bulb syringe is clean and free from contaminants. Avoid using excessive force or pressure‚ as this can damage the eardrum or push wax further into the canal. Position the patient correctly‚ with the affected ear up‚ to facilitate the flow of water and debris. Always examine the ear before and after the procedure to assess for any abnormalities. Using ear drops to soften cerumen beforehand can reduce the risk of complications. Proper training and adherence to guidelines are essential to ensure a safe and effective procedure.

Post-Irrigation Care and Follow-Up
After ear irrigation‚ patients should keep the ear dry and avoid inserting objects. Monitor for signs of infection or discomfort. Prescribed ear drops may be recommended. Schedule a follow-up appointment to ensure complete cerumen removal and proper healing. Proper post-care ensures optimal outcomes and prevents complications.
5.1 Patient Instructions for Home Care
After ear irrigation‚ patients should avoid submerging the ear in water and refrain from inserting cotton swabs or other objects. Keeping the ear dry helps prevent infections. Patients should use prescribed ear drops as directed and monitor for signs of infection‚ such as redness‚ swelling‚ or discharge. They should also report any persistent discomfort‚ dizziness‚ or hearing changes to their healthcare provider. Proper home care ensures the ear heals correctly and reduces the risk of complications; Clear instructions and adherence to these guidelines are essential for a successful recovery and to maintain ear health following the procedure.
5.2 Monitoring for Potential Side Effects
After ear irrigation‚ patients should monitor for potential side effects such as dizziness‚ ear pain‚ or discharge. These symptoms may indicate complications like infections or trauma. It is crucial to observe the ear for redness‚ swelling‚ or drainage‚ as these could signify an infection. Patients should report any unusual symptoms or persistent discomfort to their healthcare provider promptly. Monitoring for up to 48 hours post-procedure is recommended to ensure no adverse reactions occur. Early detection of side effects allows for timely intervention‚ preventing long-term issues. Proper monitoring ensures patient safety and optimal recovery outcomes following the ear irrigation procedure.
5.3 Scheduling a Follow-Up Appointment
Scheduling a follow-up appointment is essential to ensure the ear irrigation procedure was successful and to address any unresolved issues. Patients should be advised to return for a check-up within 1-2 weeks post-procedure. During this visit‚ the healthcare provider will reassess the ear canal to confirm the removal of cerumen and check for any signs of complications. This follow-up also provides an opportunity to address patient concerns and monitor healing progress. If symptoms persist or worsen‚ further evaluation or treatment may be necessary. Ensuring a follow-up appointment helps in managing potential complications early and confirming the effectiveness of the ear irrigation procedure.

Common Complications and Their Management
Common complications include ear trauma‚ infection‚ or discomfort. Management involves monitoring symptoms‚ prescribing antibiotics if needed‚ and providing further treatment to address any unresolved issues promptly.
6.1 Recognizing Signs of Ear Trauma
Signs of ear trauma post-irrigation include pain‚ redness‚ swelling‚ or bleeding in the ear canal. Hearing loss‚ tinnitus‚ or discharge may also indicate damage. Immediate medical attention is crucial if these symptoms arise. A thorough examination by a healthcare provider is necessary to assess the extent of injury. Proper wound care and pain management are typically prioritized. In severe cases‚ antibiotics may be prescribed to prevent infection. It is essential to monitor the patient closely and address any complications promptly to avoid long-term damage. Early intervention can significantly improve outcomes and restore normal ear function. Always seek professional evaluation if trauma is suspected.
6.2 Managing Infection or Discomfort Post-Irrigation
Post-irrigation infections or discomfort require immediate attention to prevent complications. Prescribed ear drops or antibiotics may be necessary to treat infections. Pain relief medications can alleviate discomfort. Patients should avoid inserting objects into the ear and keep the area clean. Monitoring for signs of infection‚ such as redness‚ swelling‚ or discharge‚ is crucial. If symptoms persist or worsen‚ a healthcare provider should be consulted promptly. Proper wound care and follow-up appointments ensure effective management and prevent long-term damage. Educating patients on post-procedure care helps in early detection of issues. Timely intervention is key to resolving infections and restoring ear health. Always prioritize professional guidance for optimal recovery outcomes.

Documentation and Reporting
Accurate documentation of the ear irrigation procedure‚ including outcomes and complications‚ is essential. Results and patient responses must be recorded and shared with healthcare providers for continuity of care.
7.1 Recording the Procedure and Outcomes
Accurate documentation of the ear irrigation procedure is essential for maintaining patient records. Detailed notes should include the extent of cerumen removal‚ any complications encountered‚ and the patient’s immediate response. This documentation ensures continuity of care and provides a reference for future treatments. All findings should be recorded in the patient’s file‚ either digitally or in hard copy‚ and stored securely to maintain confidentiality. The documentation should also reflect the patient’s condition before and after the procedure‚ including any follow-up recommendations. Proper recording of outcomes helps in assessing the effectiveness of the irrigation and informs future care decisions.
7.2 Sharing Results with Healthcare Providers
Sharing the outcomes of ear irrigation with other healthcare providers ensures comprehensive patient care. Results should be communicated clearly‚ detailing the success of the procedure‚ any remaining cerumen‚ or complications. This collaboration helps in formulating further treatment plans. Documentation should be shared securely‚ adhering to confidentiality guidelines. Verbal communication can also be used in urgent cases to inform referring physicians or specialists. Sharing results promotes a coordinated approach‚ ensuring all healthcare providers are informed about the patient’s status. This teamwork enhances patient outcomes and supports ongoing management of ear health. Effective communication is vital for maintaining continuity and quality in patient care.
Ear irrigation‚ when performed correctly‚ safely removes cerumen‚ improving hearing and preventing infections. Always adhere to guidelines and seek professional advice for optimal outcomes and patient safety.
8.1 Best Practices for Ear Irrigation
Ear irrigation should only be performed by trained healthcare professionals using proper equipment like bulb syringes. Use warm water to avoid causing trauma. Always assess the patient for contraindications‚ such as a perforated eardrum. Stop immediately if pain occurs. Avoid using hard objects to prevent injury. Patient education on post-procedure care is essential. Document the procedure and outcomes for continuity of care. Follow guidelines to minimize risks and ensure effective cerumen removal. Regular training for practitioners is recommended to maintain safety standards. Proper infection control measures must be in place. Referral to specialists is advised for complex cases or complications.
8.2 The Role of Healthcare Providers in Ensuring Safe Procedures
Healthcare providers play a crucial role in ensuring the safety and efficacy of ear irrigation procedures. Proper training and adherence to established guidelines are essential for minimizing risks. They must conduct thorough patient assessments to identify contraindications and use appropriate equipment like bulb syringes. Maintaining infection control protocols is vital to prevent complications. Providers should educate patients on post-procedure care and monitor for potential side effects. Effective documentation and communication with other healthcare professionals ensure continuity of care. Regular updates on best practices and continuous professional development are necessary to stay informed. By following these steps‚ healthcare providers can ensure safe and effective ear irrigation outcomes for their patients.

